Abstract
A practical and effective strategy for loading hydrophobic anticancer agents within the inside and outside oleic acid layer of Rubik-like magnetic nanoassemblies (MNAs) is established. In this strategy, four individual oleic acid-capped iron oxide nanocubes and dioleate-modified polyethylene glycol are assembled into cluster with high drug loading capability, high magnetism, as well as rapid and extended release behavior. After loading model drug paclitaxel (PTX), PTX-MNAs show greater antitumor activity both in vitrocell culture and in vivo animal trials compared with the same dose of free PTX (Taxol). With high uptake by tumor cells, MNAs exhibit in tumor imaging by magnetic resonance imaging. These outstanding properties are largely due to the drug delivery systems that take high drug-loading capability and high magnetism into consideration in a nano-dimension for maximizing the nanotheranostic functions and minimizing the toxic side effects. In summary, the Rubik-like magnetic nanoassemblies may have the potential to realize “all-in-one” nanotheranostic strategy to detect, diagnose, treat, and monitor tumors and therapeutic response in further pre-clinical and clinical studies.
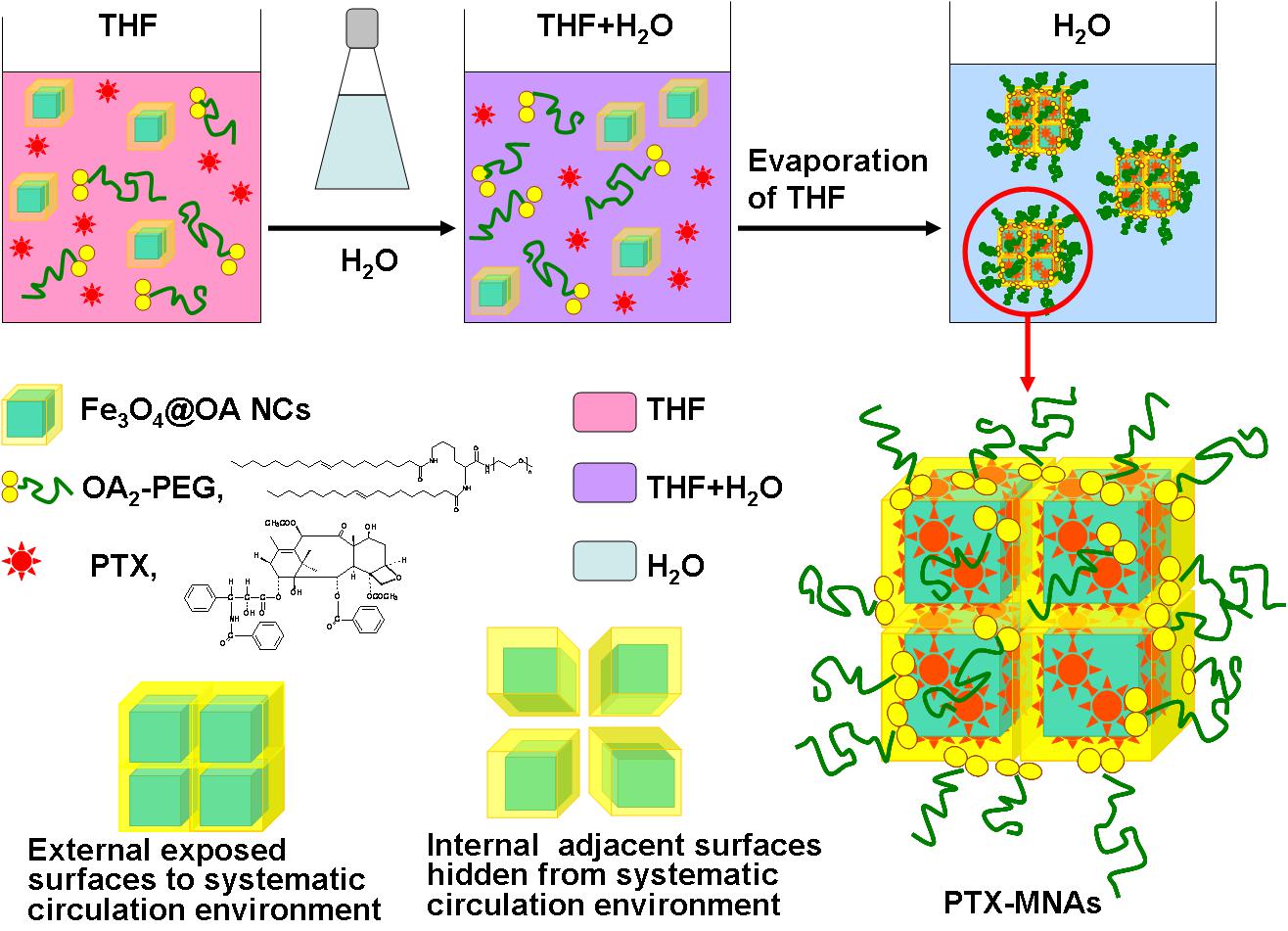
Fig. 1. Schematic representing formulation and structure of Rubik like PTX-MNAs. Upon encapsulation in nanoassemblies, the hydrophobic PTX was inserted in the oleic acid cap of Fe3O4@OA NCs. The polymers were anchored on the surface of Rubik cube like nanoassemblies by the hydrophobic interaction between oleic acid cap of Fe3O4 NCs and oleic acid terminal of amphiphilic polymers.
Fei Xiong, Caiyun Yan, Yuejian Chen, Jianxiang Chen, Bingya Yang, Yu Zhang, Huile Gao, Zichun Hua, Ning Gu*, Rubik-like magnetic nanoassemblies as an efficient drug multifunctional carrier for cancer theranostics. J. Control. Rel., 172(3): 993-1001, 2013.

